70s Fighter Jets - This article needs additional references for review. Please help improve this article by adding citations to trusted sources. Unsourced content can be challenged and removed. Search source: "aircraft intercept" – news newspapers books academics JSTOR (June 2020 ) (learn how to delete this template text)
Convair F-106 Delta Dart US Air Force flagship interceptor in the 1960s, 70s and 80s.
70s Fighter Jets

Intercept aircraft Or simply called the interceptor. It is a type of fighter aircraft specially designed for a defensive role against offensive AMI aircraft, especially bombers and reconnaissance aircraft. Aircraft that can or operate as 'standard' fighters and air interceptors are sometimes referred to as interceptors. There are two general classes of interceptors:
Cockpit From 70s Fighter Aircraft Finds New Home At Aviation Museum
Light fighter Designed for high performance in the short term and heavy fighter aircraft Intended to operate at long distances in competitive airspace and adverse weather conditions. while the latter has been exemplified in the past by specialized night fighter and all-weather interceptor designs. Since the 1960s, the integration of air refueling satellite navigation system aircraft radar and an Out of Sight Range (BVR) missile system for more frontline fighters. Designed to fill roles previously reserved for special night/all-weather fighters.
For daytime operations Conventional light fighters often act as interceptors. Daytime interceptors have been used in defensive roles since World War I, and are perhaps best known from major operations such as the Battle of Britain, where the Supermarine Spitfire and Hawker Hurricane were part of the defensive maneuver that was fought. Successful, however, dramatic improvements in ground and air radar have made existing fighters more flexible. and some later designs were viewed exclusively as daylight interceptors. (exceptions include The Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet, the only rocket-powered manned military aircraft to see combat. at a lower level Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-15, which is heavily armed specifically for anti-bomber operations (also intercepts a special day)
Night fighters and bomber destroyers are heavy interceptors. Although rarely mentioned in the beginning. The combination of jet-powered bombers and nuclear weapons during the early Cold War era led the Air Force to demand more capable interceptors. The word is perhaps the most well-known and used during this time. Examples of classic interceptors from this era include the Convair F-106 Delta Dart, Sukhoi Su-15, and the Glish Electric Lightning.
In the 1960s and 1970s, rapid improvements in design led to greater air superiority. And most fighters, such as the Grumman F-14 Tomcat and McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle, can perform point defense interceptors and tactical threats shift from bombers to intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). Specifics are rare, with the Panavia Tornado ADV, Mikoyan MiG-25, Mikoyan MiG-31 and Shang J-8 being the only examples of widely used designs after the 1960s.
Did Ufos Bring Down Fighter Jet Off Uk Coast Killing American Pilot 'who Saw Flying Cone In Sky'?
The first Intercept Squadron was formed during World War I to protect London from the Zeppelin attack. and later against fixed-wing long-range bombers agencies in the early days Aircraft that have withdrawn from front-line service are often used. In particular the Sopwith Pup aircraft, they were informed of their target location prior to takeoff by Command Ctr in the Horse Guards Building. The superior Sopwith Camels took their place.
By the 1930s, the bomber's speed had increased so much that conventional interception techniques seemed impossible. Visual and audio detection from the ground is only a few miles away. This means that the interceptors will not have enough time to climb to a height before the bombers reach their targets. Standing combat aerial reconnaissance is possible only at high cost. "Bombers always get through" was the conclusion of that episode.
The invention of radar enabled early detection of long-range aircraft over a distance of 100 miles (160 km), day and night, and in all weather conditions.
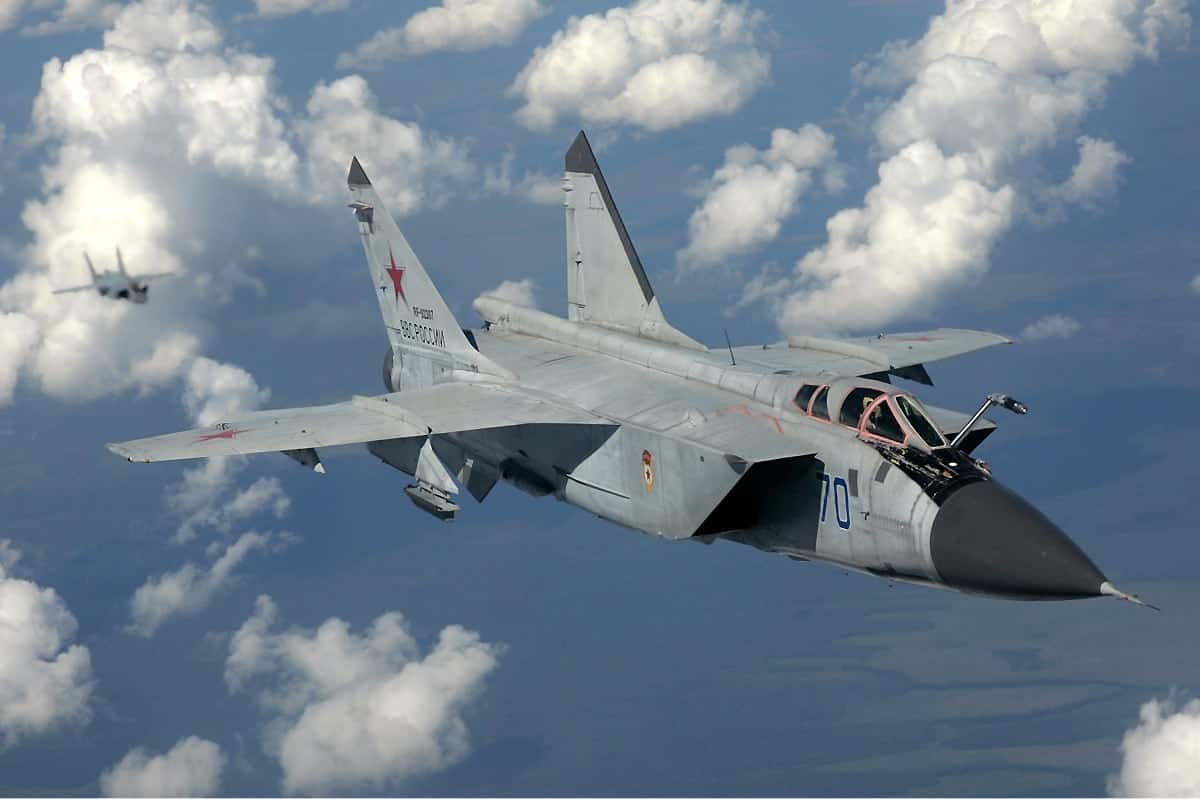

A typical bomber might take 20 minutes to cross the detection zone of early radar systems. which was enough time for the fighter interceptor to be released. climb altitude and measuring bombers Ground-controlled interceptions require constant contact between the interceptor and the ground. as long as the pilot can see the bomber And nationwide networks, such as the Dowding system, were created in the late 1930s to coordinate these efforts.
The First Jet Pilots
The launch of the jet increased its speed from 300 mph. (480 km/h) to 600 mph (970 km/h) at one point and approximately double the operating altitude. Although the radar performance has improved. But the gap between offset and offset has been greatly reduced. Massive attacks can confuse the DEF's ability to communicate with the pilot. This renders the classic ground-controlled interception methods inadequate. in the United States This led to the introduction of a semi-automated ground vironmt to computerize this task. While in the UK that has led to the use of more powerful radars to improve detection times.
The introduction of the first useful surface-to-air missiles in the 1950s eliminated the need for highly reactive interceptors. Because it can launch missiles almost instantly. Leaving point defense role for missiles Air Forces with long-range fuel have turned to much larger interceptor designs. This led to the abandonment of many short range designs such as the Avro Arrow and Convair F-102 in favor of much larger long range designs such as the North American F-108 and MiG-25.
During the Cold War of the 1950s and 1960s, a strong deterrent force was vital to opposing powers. It is the best tool to combat nuclear attack by strategic bombers. They rapidly developed speed, distance, and altitude. In the 1960s, nuclear attacks were unstoppable when hypersonic missiles were launched. 5–7 km/s from outside the atmosphere The doctrine of mutual destruction replaces defensive reinforcement. Make deterrence less strategically logical The interceptor's utility was reduced due to the superiority of heavy air combined with its role as a fighter.
Intercept missions are difficult by their nature. Consider the desire to defend a single target against long-range bomber attacks. Bombers have the advantage that mission parameters can be selected - attack vector, speed and altitude. This leads to unclear areas where invasions can occur. Interceptors must be able to launch, take off, climb altitude, dodge to attack and attacking the bomber the moment the bomber crosses the first detection range over the target.
Jordan Inks Deal For 12 Block 70 F 16s From Lockheed Martin
Dedicated interceptors sacrifice the capabilities of air superiority fighters and multi-role fighters (i.e. countering enemy fighters in air combat tactics) by optimizing their performance to increase speed and/or speed. higher As a result, interceptors often look very impressive on paper. This is often better than less numerous and slower fighter designs. The same "low ability" due to limited maneuverability. especially at high altitudes and low speeds.
Across the spectrum of limitations The design approach demonstrates the sacrifices necessary to achieve critical decency. Especially in terms of performance selection is the "Point Defiance Interceptor".
A lightweight design, the SPD is intended to be spent most of the time on the ground on destructive targets. and can be released on demand Climb altitude, maneuver and attack in a short amount of time before dropping your bomber's weapons.
During World War II, the Luftwaffe's most important need was interceptors. As Commonwealth forces and American Air Forces attacked German targets day and night. As bombing efforts increase In particular, in early 1944, the Army introduced a rocket-propelled design. Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet in a very short-range intercept role, Jain allowed about 7 minutes of full-power flight, but were so effective that they could fly a defensive fighter fighter.
Wings Airplane Aircraft Vintage Lot World War 2 Fighter Plane Pilot Aviation 70s
However, Me 163 needs an airfield. And soon it was constantly attacked. Following the Emergency Fighter program, the Germans developed EV adder designs such as the Bachem Ba 349 Natter, which launched vertically. So no airport is required. early design These Germans proved difficult to use at Jeral. which often becomes a deadly trap for their pilots.
And had little effect on bombing. two German jet fighters enhanced with rockets; Me 262s in the "C" sub-type series, all of which are nicknamed "Home Protector" (Heimatschützer The planned He 162E used the same BMW 003R turbojet/rocket "mixed power" gain as the Me 262C-2b Heimatschützer II, but was never mass produced.
At the beginning of the Cold War The bomber was expected to fly higher and faster. Early transsonic and supersonic fighters There is a modestly sized internal fuel tank in the slim body. but high fuel consumption This underscores the acceleration and operational ceiling of the prototype fighter. Ready to sacrifice time to stop the car. Essentially limiting them to that point.
Second degree assault washington state, 2nd degree assault sentence, 2nd degree aggravated assault, 2nd degree assault mn, 2nd degree assault, 2nd degree assault definition, 3rd degree assault washington state, 4th degree assault washington state, 2nd degree felony assault, 4th degree assault washington, what is assault 2nd degree, 2nd degree assault charges